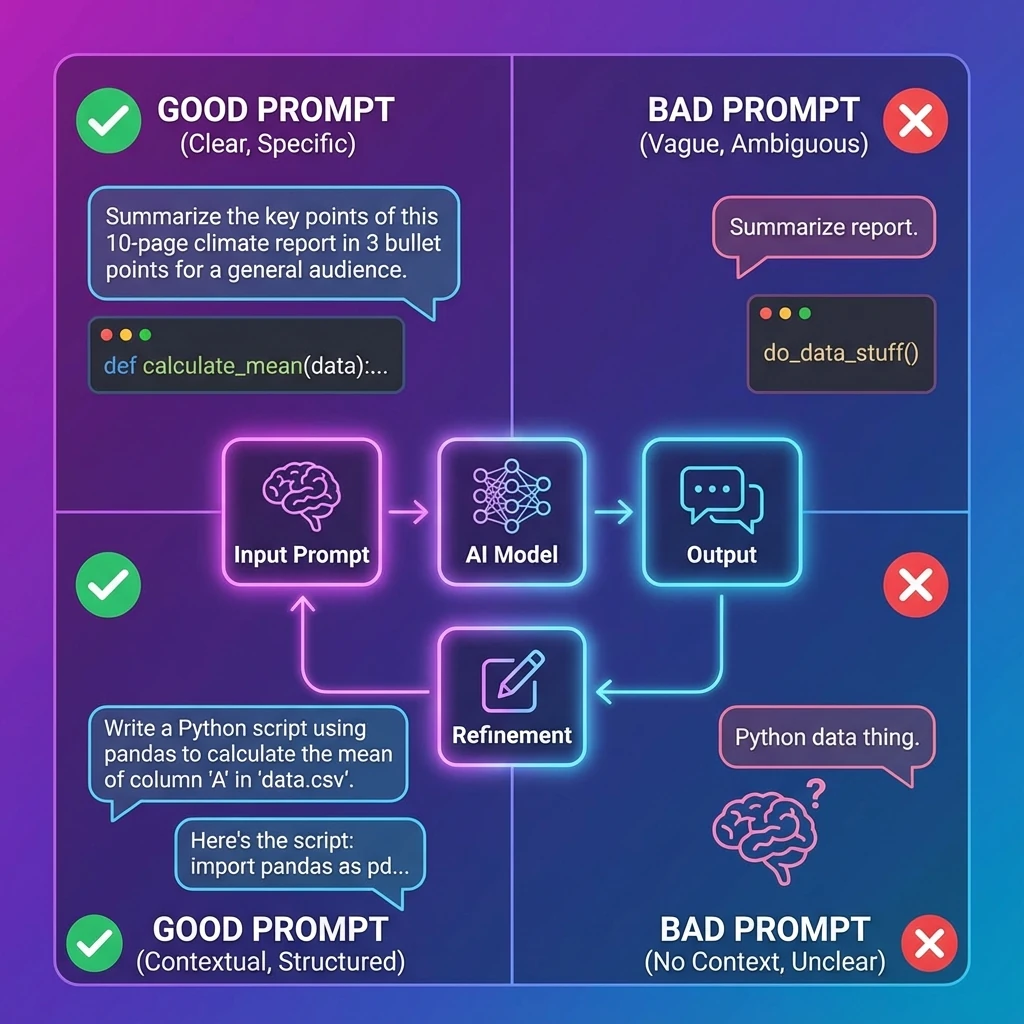
Why Prompt Engineering Matters in 2026
AI models are smarter than ever, but they're only as good as your prompts. The difference between a vague prompt and a well-engineered one:
Bad Prompt:
"Write a blog post about AI"
Result: Generic 300-word article, no depth, boring
Good Prompt:
"Write a 2000-word blog post about AI's impact on healthcare. Target audience: hospital administrators. Include 3 real-world case studies, ROI data, and implementation challenges. Use professional but accessible tone. Structure: intro, 3 main sections, conclusion with actionable steps."
Result: Detailed, actionable, professional article with specific examples
The difference? Specificity, context, and structure.
The 5 Core Principles of Prompt Engineering
1. Be Specific
Vague prompts = vague outputs. Always include:
- What: Exact task
- Who: Target audience
- How: Format, tone, length
- Why: Purpose/goal
Example:
❌ Bad: "Explain quantum computing"
✅ Good: "Explain quantum computing to a 10-year-old using simple analogies. Focus on how it's different from regular computers. 200 words max."
2. Provide Context
AI doesn't know your background. Give it context:
Example:
❌ Bad: "Write code for user authentication"
✅ Good: "I'm building a Next.js app with Supabase backend. Write TypeScript code for user authentication using email/password. Include error handling, password hashing, and JWT token generation. Follow Next.js 14 best practices."
3. Use Examples (Few-Shot Prompting)
Show the AI what you want:
Example:
Convert these product descriptions to marketing copy:
Example 1:
Input: "Blue t-shirt, cotton, size M"
Output: "Stay cool and comfortable in our premium cotton tee. Classic blue color pairs with anything. Perfect fit guaranteed."
Example 2:
Input: "Wireless mouse, ergonomic, 2.4GHz"
Output: "Work smarter with our ergonomic wireless mouse. 2.4GHz connection ensures zero lag. Your wrist will thank you."
Now convert:
Input: "Laptop stand, aluminum, adjustable"
Output:4. Break Down Complex Tasks (Chain-of-Thought)
For complex problems, ask AI to think step-by-step:
Example:
❌ Bad: "Calculate the ROI of implementing AI chatbots"
✅ Good: "Calculate ROI of AI chatbots for customer service. Think step-by-step:
1. List typical costs (setup, maintenance, training)
2. List typical savings (reduced support staff, faster response times)
3. Calculate break-even point
4. Provide 3-year ROI projection
Show your work for each step."
5. Specify Output Format
Tell AI exactly how to structure the response:
Example:
❌ Bad: "Compare Python and JavaScript"
✅ Good: "Compare Python and JavaScript. Output as a markdown table with these columns: Feature, Python, JavaScript, Winner. Include rows for: Speed, Learning Curve, Job Market, Web Development, Data Science, Syntax."
Advanced Techniques
Technique 1: Role-Playing
Assign AI a specific role for better context:
"You are a senior software architect with 15 years of experience in microservices. Review this system design and identify potential bottlenecks, security issues, and scalability concerns. Provide specific recommendations for each issue."Technique 2: Iterative Refinement
Start broad, then refine:
Prompt 1: "List 10 blog post ideas about AI in education"
Prompt 2: "Expand idea #3 into a detailed outline with 5 main sections"
Prompt 3: "Write section 1 in 500 words, targeting K-12 teachers"
Technique 3: Constraint-Based Prompting
Add constraints to force creativity:
"Write a product description for noise-cancelling headphones. Constraints:
- Exactly 100 words
- No technical jargon
- Include emotional benefit
- End with call-to-action
- Use power words: transform, effortless, premium"Technique 4: Negative Prompting
Tell AI what NOT to do:
"Explain blockchain to beginners.
DO NOT:
- Use technical terms without explaining them
- Assume prior knowledge of cryptography
- Make it longer than 300 words
- Use analogies involving finance (too confusing)
DO:
- Use everyday analogies
- Include a simple diagram description
- Focus on practical use cases"Prompt Templates for Common Tasks
Template 1: Content Writing
Write a [word count] [content type] about [topic].
Target audience: [audience]
Tone: [professional/casual/humorous/etc]
Goal: [inform/persuade/entertain]
Include:
- [specific element 1]
- [specific element 2]
- [specific element 3]
Structure:
- [section 1]
- [section 2]
- [section 3]Template 2: Code Generation
Write [language] code for [functionality].
Context:
- Framework: [framework]
- Database: [database]
- Requirements: [requirements]
Include:
- Error handling
- Input validation
- Comments explaining logic
- Type safety (if applicable)
Follow [style guide] best practices.Template 3: Data Analysis
Analyze this data: [data]
Questions to answer:
1. [question 1]
2. [question 2]
3. [question 3]
Output format:
- Summary (3 bullet points)
- Detailed analysis for each question
- Visualizations (describe what charts to create)
- Actionable recommendationsModel-Specific Tips
ChatGPT (GPT-4o)
- Strength: Creative writing, brainstorming
- Best for: Content creation, code explanations
- Tip: Use "Let's think step-by-step" for complex reasoning
Claude (Anthropic)
- Strength: Long-form content, analysis
- Best for: Research, document summarization
- Tip: Provide extensive context (Claude handles 200K tokens)
Gemini (Google)
- Strength: Factual accuracy, real-time data
- Best for: Research, fact-checking
- Tip: Ask for sources and citations
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Being Too Vague
Bad: "Help me with my project"
Good: "Review my React component for performance issues. Focus on unnecessary
re-renders and memory leaks."
2. Asking Multiple Questions at Once
Bad: "Explain AI, machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks"
Good: "Explain AI in 200 words. Then I'll ask about machine learning separately."
3. Not Iterating
First response not perfect? Refine your prompt instead of giving up.
4. Ignoring Context Window
Long conversations lose context. Summarize previous discussion in new prompts.
Practice Exercises
Exercise 1: Improve This Prompt
Bad Prompt: "Write about social media"
Your Task: Rewrite it using the 5 core principles
Solution: "Write a 1500-word article about social media's impact on mental health for parents of teenagers. Include 3 peer-reviewed studies, practical tips for limiting screen time, and warning signs of social media addiction. Tone: empathetic but evidence-based. Structure: intro, problem overview, research findings, solutions, conclusion."
Exercise 2: Create a Chain-of-Thought Prompt
Task: Calculate whether it's worth buying a $50,000 electric car vs $30,000 gas car
Your Prompt: Break it down step-by-step (fuel savings, maintenance, insurance, resale value, environmental impact)
Tools to Improve Your Prompts
- PromptPerfect: AI-powered prompt optimizer
- PromptBase: Marketplace for tested prompts
- ChatGPT Prompt Generator: Meta-prompting tool
- Anthropic Prompt Library: Claude-specific examples
The Future of Prompt Engineering
Trend 1: Multimodal Prompts
Combine text, images, and audio in prompts. Example: "Analyze this screenshot and suggest UI improvements"
Trend 2: Automated Prompt Optimization
AI tools that automatically improve your prompts (like PromptPerfect)
Trend 3: Domain-Specific Prompting
Specialized prompts for legal, medical, financial use cases
Key Takeaways
🎯 Master These 5 Principles
- Be Specific: What, who, how, why
- Provide Context: Background, constraints, goals
- Use Examples: Show, don't just tell
- Break Down Tasks: Step-by-step reasoning
- Specify Format: Exact output structure
Practice Daily: The more you prompt, the better you get. Start with templates, then customize.